-
Byzantine Fault Tolerance in Blockchain: A Closer Look
 George Georgiev
George Georgiev 2022-11-02
2022-11-02 3419
3419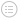 Crypto wiki
Crypto wiki
-
Summary:Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) is a term tossed around quite often. Here’s a closer look at what it means and how it applies to blockchain.
In the past few years, the digital currency industry has expanded significantly. The rise of the latest project also shows that real estate developers have various means to deal with current problems in this field.
One of the frequently mentioned terms is "BFT consensus mechanism". BFT means Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism, which gives a basic theoretical problem in electronic computer systems that existed long before BTC.
However, many protocols based on the blockchain are focused on dealing with problems related to Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism, and the following will conduct in-depth analysis on this problem and various problems arising from it.
Expression of Byzantine General's Difficulty
The key of Byzantine General is one of the most discussed basic theoretical problems, no matter when the consensus discussion topic is explicitly put forward.
In 1982, an article namedByzantine General's ProblemAshley Lampert, Johnson Shostak, and Marshall Eto. The graduation thesis wrote:
A reliable electronic computer system must be able to solve the common faults of one or several components. It is very likely that the common fault components show a behavior that is often ignored, that is, they push contradictory information to some parts of the system differences. Dealing with such unsuccessful problems is abstractly described as the Byzantine General's Problem.
The name comes from the contrast in the article. More specifically, the creator described a basic theoretical situation, that is, several divisions of Byzantine troops camped outside the enemy city. Each division is guided by its own famous generals, all of whom are stationed in different bases. Commanders must develop a common plan (attack or evacuation), and they can only rely on information for communication. However, some senior generals may be traitors and try to prevent loyal senior generals from reaching consensus.
Therefore, the senior generals must do everything possible to ensure that:
- All the loyal generals decided on the same plan.
- Few traitors should not let loyal generals adopt bad plans.
The system that can solve the above problems is considered to have Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism (BFT). This is the origin of BFT consensus algorithm.
In essence, Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism is a standard to prevent the system from being subjected to untrustworthy (disloyal) participants.
Dealing with the problem of Byzantine generals
In order to solve the problem of Byzantine generals and realize Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism (BFT), senior generals must reach most agreements in terms of overall development strategy.
It mainly depends on the system and importance to complete by various means. In the general environment of blockchain, both work unit certification and interest certification can realize Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism, but the two methods are different.
Most of the rights and interests prove that the blockchain can tolerate up to one third of the connection points being abnormal, and also3 in 1Where F is the total number of disloyal nodes, the formula calculation proposes the number of faithful nodes that the system must have.
For example, in a system with four nodes, only one of the connection points is likely to have an exception, which cannot meet the specification (3f 1).
In February 1999, Miguel Castro and Barbara Liskov, the Electronic Information Science Laboratory of MIT, published a paper based on the so-calledIt is easy to use Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism.
How does blockchain solve the problem of Byzantine generals?
According to the professional technology of the blockchain, it has brought a variety of solutions to the Byzantine General's problem. The difference comes from the specified consensus algorithm and BFT method, but the proof of work or the proof of rights and interests bring workable solutions.
How does BTC solve the problem of Byzantine generals?
Interestingly, in the initial industry report, the quantum chain did not mention the Byzantine General's problem, but with the introduction of BTC Internet, most of the pseudonym originators overcame this situation based on the PoW consensus algorithm.
In order to get rid of the dilemma, Satoshi created a way to apply password security and public key encryption in the digital network. In order to avoid forgery of data information, hach is used as the data encryption security factor, and the identity of Internet users is authenticated using their public keys.
Transaction management is used for protection in blocks. Such blocks use their hash values to transmit to other blocks, and are protected by data encryption. It should be noted that the blockchain applies Merkle tree to check the hach from the genesis (original) block. Each block from the genesis block is useful. This blockchain is authenticated by mining. These people deal with the difficulty of login password in the market to create a blockchain as part of the consensus approach.
BTC has established an established and objective standard guide for the blockchain to get rid of the Byzantine general's problem. Internet members must publish the relevant certificates of their work tasks before they can add information to the blockchain (thus, the certification of the work unit). This would be very costly for Member States and would make them unwilling to share incorrect information, as other Member States would argue against such incorrect information.
All standards are established and objective, which means that information cannot be forged.
How to solve the problem of Byzantine generals?
The management method network of consensus algorithm confirmed by shares does not rely on mining, but depends on shares. To become a network verification system operator, customers must invest in the system. People with more shares can also authenticate a large number of blockchains and obtain more rewards. Those who try to forge information are likely to lose their chips.
This systematic approach to solving problems varies. For example, Ethercoin 2.0 uses the Casper optimization algorithm. Before building a special block and importing it to the Internet, it requires at least two-thirds of all nodes to allow special blocks.
According to the importance of the system and the team approach, try to solve problems in a variety of ways. For example, it is much faster to reach an agreement by using the certificate of entitlement (dPoS). On the other hand, some systems have completed the useful Byzantine fault-tolerant mechanism.
Disclaimer:As an open information publishing platform, shilian only represents the author's personal views and has nothing to do with shilian. If the article, picture, audio or video contains infringement, violation or other inappropriate remarks, please provide relevant materials and send it to: 2785592653@qq.com.
Hint:The information provided on this site does not represent any investment suggestion. Investment is risky, and you must be cautious when entering the market.
ShilianFan group:Provide the latest hot news, airdrop candy, red envelopes and other benefits, WeChat: rtt4322.